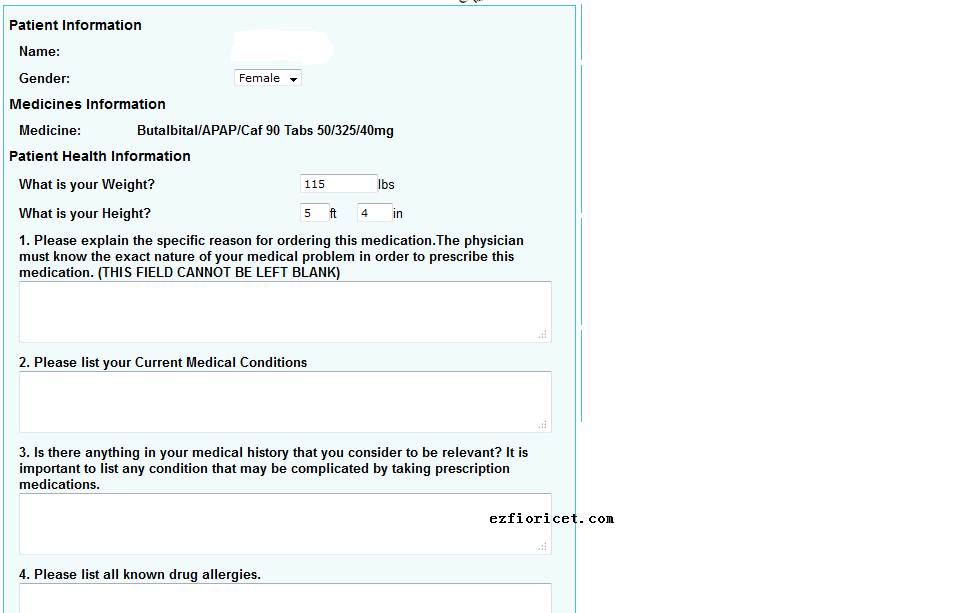
There is a very long health questionnaires you should answer when you order fioricet online. It includes almost all aspects of your health condition, medical conditions, and you any kinds of diseases. It includes:
1. your sex
2. your weight;
3. your height
4. your BMI will be calculated according to your weight and your height;
5. why you order or buy fioricet online ?
6. your health conditions;
7. your medical conditions;
8. your health history;
9. your family health history;
10. your family medical history;
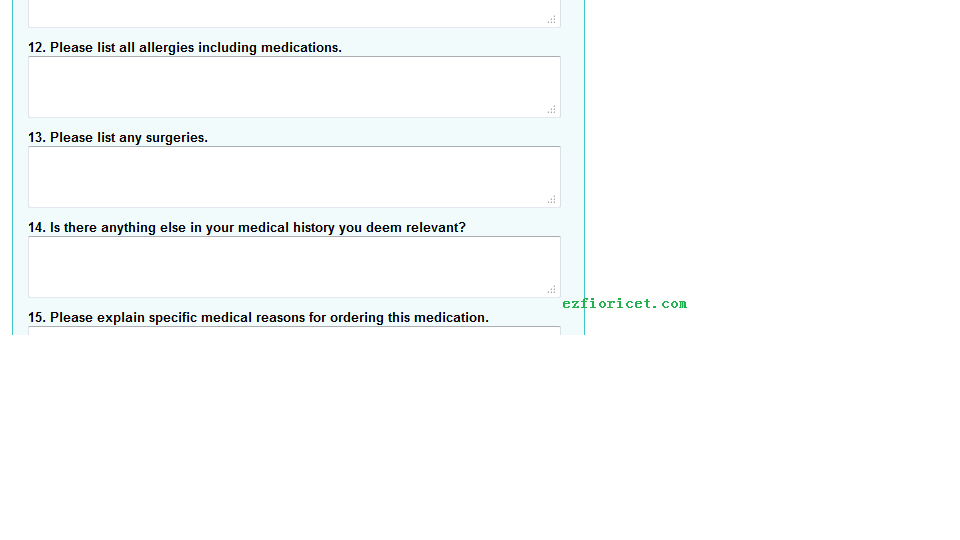
11. your allergy;
12. your surgeries;
13. which drugs are you taking;
14. which drugs you are planning to taking
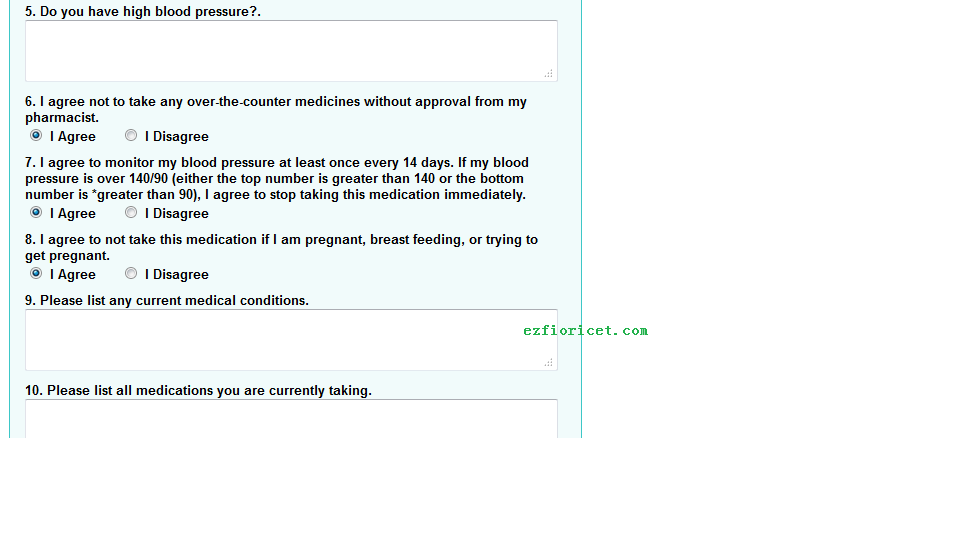
15. high blood pressure;
16. some agreement you must follow (Monitor blood pressure, not take fioricet is pregnant or breast feeding)
17. you must know your responsibility when you take fioricet
18. a lot of other detail about your ED, or nitroglycerin something ..
…
Our health questionnaires have already designed for all the following questions.You just complete our health questionnaires here, we will complete the form according to your health and medical conditions.
For more detail, please check the pictures:
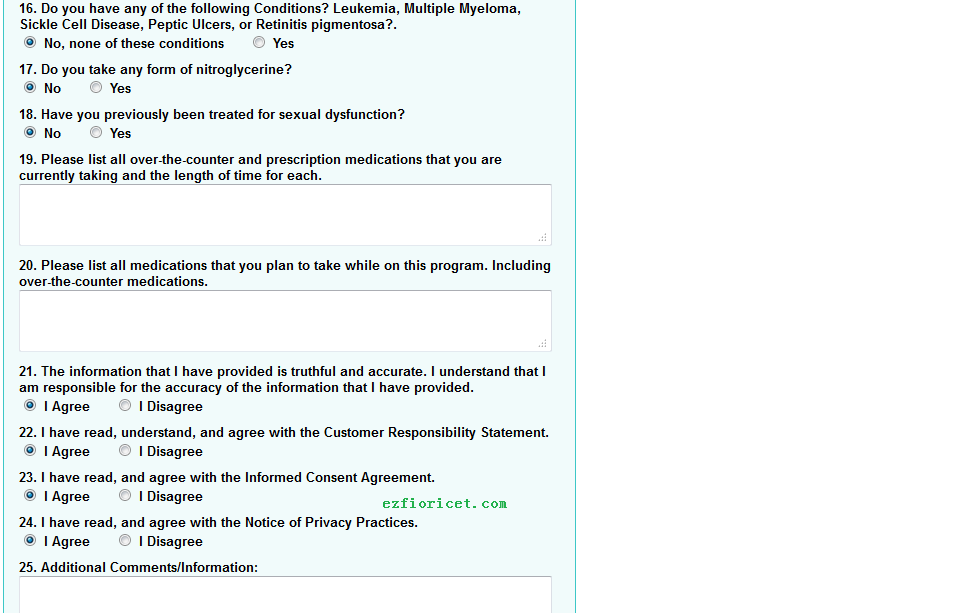
When ordering Fioricet (or any prescription medication) online, it’s essential to approach the process carefully, ensuring you’re using a legitimate and reputable source.
While discussing Fioricet with a doctor (either in person or through a telemedicine service), you should provide complete and honest information to ensure safe use of the medication.
Here are the key things to tell your doctor:
1. Your Medical History
- Liver conditions: Since Fioricet contains acetaminophen, you should inform the doctor if you have any history of liver disease (e.g., cirrhosis, hepatitis) or if you drink alcohol regularly, as this increases the risk of liver damage.
- Kidney problems: Fioricet can strain the kidneys, so if you have a history of kidney disease or reduced kidney function, it’s important to disclose this.
- Respiratory issues: Let your doctor know if you have conditions like asthma, COPD, or other breathing problems, as butalbital can cause respiratory depression.
- History of depression or mental illness: If you have ever been diagnosed with depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, or have had suicidal thoughts, this information is critical since butalbital can worsen these conditions.
- History of substance abuse or addiction: Tell the doctor if you have a history of drug or alcohol abuse, as Fioricet contains butalbital, which is a habit-forming barbiturate and could lead to dependency or misuse.
- Stomach or gastrointestinal issues: Mention if you have a history of ulcers, gastritis, or acid reflux, as Fioricet’s caffeine component can exacerbate these conditions.
- Allergies: Notify your doctor if you have any known allergies to acetaminophen, butalbital, caffeine, or other medications.
2. Current Medications
- Over-the-counter (OTC) medications: Inform your doctor if you are taking any other OTC medications, particularly pain relievers or medications containing acetaminophen, to avoid exceeding the recommended daily dose.
- Prescription medications: Mention all prescription medications you are taking, especially:
- Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin): Acetaminophen can interact with blood thinners, increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Opioids, sedatives, or other CNS depressants: Butalbital can enhance the sedative effects of these medications, leading to dangerous drowsiness or respiratory depression.
- MAO inhibitors (antidepressants): Combining Fioricet with these can cause severe interactions.
- Benzodiazepines or antidepressants: The sedative effects of butalbital can be heightened when combined with these drugs.
- Other medications containing caffeine: Mention if you take any caffeine-containing medications or supplements to avoid overstimulation.
3. Frequency of Headaches
- Provide a detailed account of your headache frequency, duration, and severity. The doctor will need to determine whether your condition justifies a prescription for Fioricet. For example:
- How many headaches you experience per week or month.
- How long they last.
- What triggers your headaches (e.g., stress, tension, lack of sleep).
4. Previous Treatments
- Tell your doctor what treatments you’ve tried in the past for headaches, including:
- OTC pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen, aspirin).
- Prescription medications for migraines or tension headaches.
- Alternative therapies (e.g., massage, acupuncture).
- Explain how effective (or ineffective) these treatments have been for your condition.
5. Caffeine Intake
- Provide information about your caffeine consumption (e.g., coffee, energy drinks, tea), as Fioricet contains caffeine, and excessive intake can lead to side effects like jitteriness, increased heart rate, or anxiety.
6. Alcohol Consumption
- Be honest about your alcohol use. Drinking alcohol while taking Fioricet increases the risk of liver damage (due to acetaminophen) and CNS depression (due to butalbital). Let the doctor know how much and how often you drink.
7. Use of Other Headache Medications
- If you take other medications for headaches, such as triptans for migraines, provide this information, as your doctor will want to avoid drug interactions or overuse of pain relievers, which can lead to rebound headaches.
8. Pregnancy or Breastfeeding
- Let your doctor know if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding, as Fioricet is generally not recommended in these cases. Butalbital can pass through the placenta and breast milk, potentially harming the baby.
9. Potential for Dependency
- Discuss any concerns you have about dependence or addiction. Since Fioricet contains butalbital, which can be habit-forming, your doctor needs to know if you’re concerned about becoming reliant on the medication.
10. Any Concerns About Ordering Online
- If you are ordering Fioricet online, make sure to confirm with the doctor if it is safe and legal to do so. It’s critical that you:
- Use a legitimate online pharmacy that requires a valid prescription.
- Avoid unregulated sources that could sell counterfeit or unsafe medications.
Key Points to Discuss with Your Doctor When Ordering Fioricet:
- Medical history (liver/kidney disease, respiratory issues, mental health, substance abuse).
- Current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Frequency and severity of headaches.
- Previous treatments tried and their effectiveness.
- Caffeine and alcohol consumption.
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding status.
- Concerns about potential addiction.
By sharing this information, you ensure your doctor can prescribe Fioricet safely and appropriately based on your medical history and current condition.












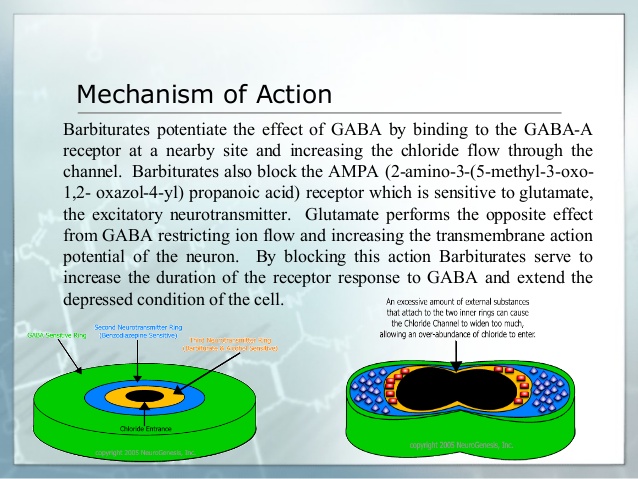
 Butalbital is in a group of drugs called barbiturates. It relaxes muscle contractions involved in a tension headache.
Butalbital is in a group of drugs called barbiturates. It relaxes muscle contractions involved in a tension headache.
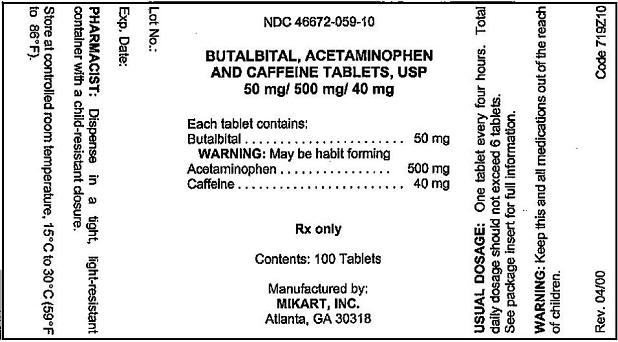



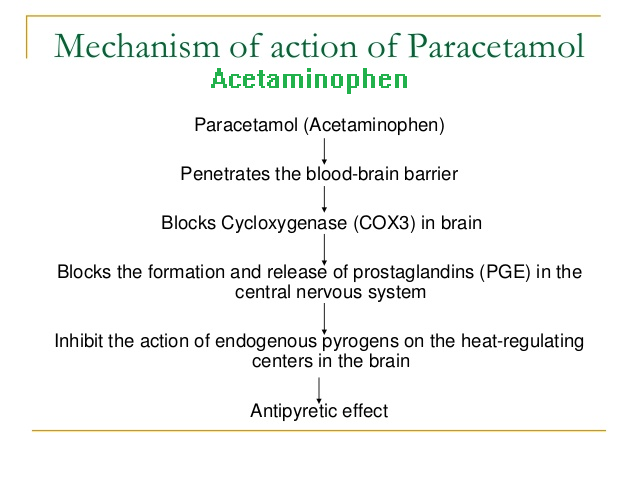 Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen acts primarily in the CNS and increases the pain threshold by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, an enzyme involved in prostaglandin (PG) synthesis. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is generally considered to be a weak inhibitor of the synthesis of prostaglandins (PGs). However, the in vivo effects of paracetamol are similar to those of the selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. Paracetamol also decreases PG concentrations in vivo, but, unlike the selective COX-2 inhibitors, paracetamol does not suppress the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis. Acetaminophen inhibits both isoforms of central cyclooxygenase, COX-1 and COX-2.
Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen acts primarily in the CNS and increases the pain threshold by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, an enzyme involved in prostaglandin (PG) synthesis. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is generally considered to be a weak inhibitor of the synthesis of prostaglandins (PGs). However, the in vivo effects of paracetamol are similar to those of the selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. Paracetamol also decreases PG concentrations in vivo, but, unlike the selective COX-2 inhibitors, paracetamol does not suppress the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis. Acetaminophen inhibits both isoforms of central cyclooxygenase, COX-1 and COX-2.