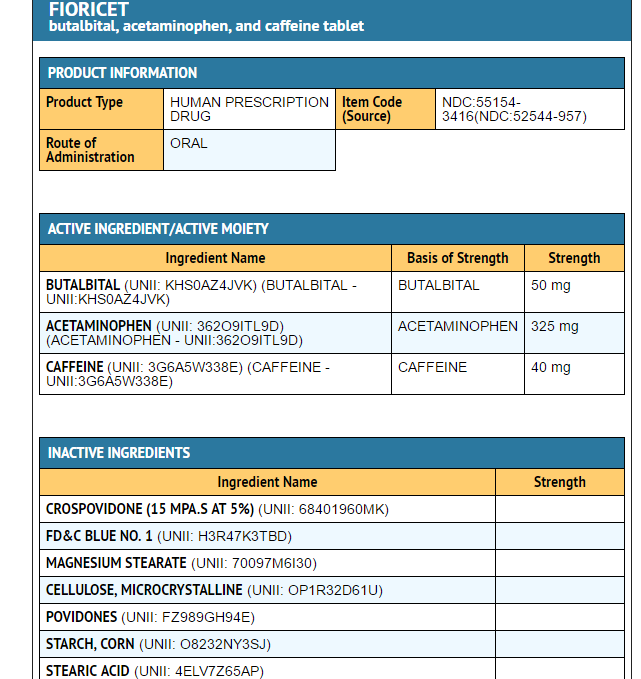
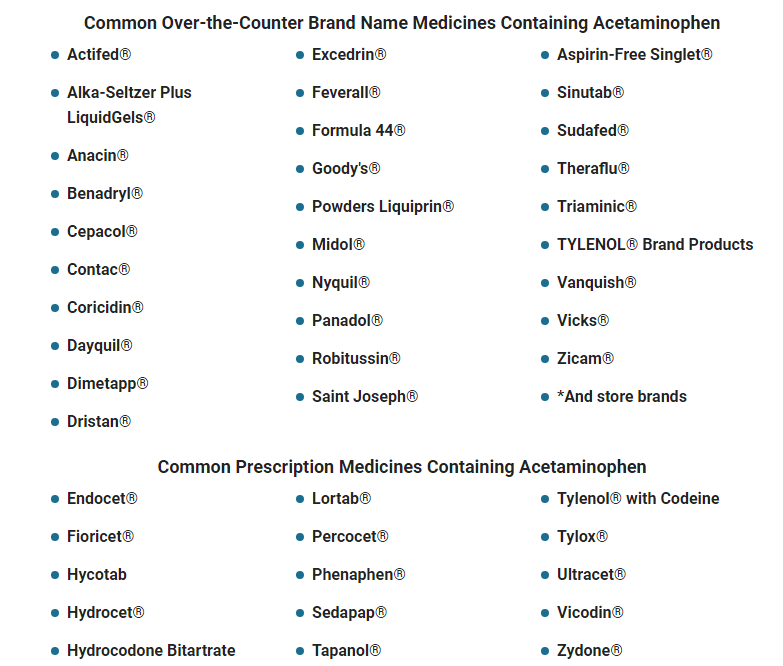
Taking Fioricet, a combination of butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine, comes with several concerns due to the potential risks associated with each of its ingredients.

Here are the main concerns when taking Fioricet:
1. Risk of Dependence and Abuse (Butalbital)
- Butalbital, a barbiturate, is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant that can cause drowsiness and relaxation. Over time, this can lead to physical dependence or psychological addiction. Fioricet has a potential for abuse, particularly in those with a history of substance use disorders.
- Stopping Fioricet abruptly after prolonged use can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including anxiety, tremors, seizures, and agitation.
2. Liver Damage (Acetaminophen)
- Acetaminophen is generally safe in recommended doses, but taking too much can lead to liver damage or even acute liver failure. The risk is higher if:
- You take more than the recommended daily dose (no more than 4,000 mg of acetaminophen for adults).
- You use Fioricet along with other medications that contain acetaminophen (e.g., cold medicines or other pain relievers).
- You consume alcohol while taking Fioricet, as this significantly increases the risk of liver toxicity.
3. Sedation and Impaired Alertness (Butalbital)
- Butalbital can cause drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination, making activities like driving, operating machinery, or performing tasks that require full attention dangerous.
- Combining Fioricet with other CNS depressants (such as benzodiazepines, opioids, or alcohol) can increase the risk of extreme sedation, respiratory depression, or even coma.
4. Rebound Headaches
- Overuse of Fioricet can lead to medication-overuse headaches (also known as rebound headaches). This occurs when the medication used to treat headaches actually causes them to occur more frequently. Regular use of Fioricet (more than two days per week) increases the risk of developing chronic headaches.
5. Gastrointestinal Issues (Caffeine)
- The caffeine in Fioricet can cause stomach upset, heartburn, or exacerbate existing gastrointestinal problems like acid reflux or ulcers.
- Caffeine can also lead to symptoms such as nervousness, jitteriness, increased heart rate, or insomnia, especially if taken in combination with other sources of caffeine (like coffee or energy drinks).
6. Respiratory Depression (Butalbital)
- Butalbital, as a barbiturate, can cause respiratory depression (slow or shallow breathing), especially at higher doses or when combined with other CNS depressants. This can be life-threatening in severe cases.
7. Risk of Overdose
- Overdose is a significant concern with Fioricet, especially due to the combined effects of its ingredients:
- Butalbital overdose can cause excessive sedation, confusion, difficulty breathing, and coma.
- Acetaminophen overdose can lead to liver failure, which may require a liver transplant or be fatal if not treated promptly.
- Caffeine overdose can cause restlessness, rapid heartbeat, or tremors.
8. Allergic Reactions
- Some individuals may experience an allergic reaction to any of the components of Fioricet, particularly acetaminophen. Symptoms may include rash, itching, swelling, dizziness, or trouble breathing. In such cases, medical help should be sought immediately.
9. Potential for Mental Health Effects
- Butalbital can affect mood, leading to feelings of depression, anxiety, or irritability in some individuals. Long-term use may increase the risk of developing depressive symptoms or even suicidal thoughts.
10. Interactions with Other Medications
- Fioricet can interact with many other medications, leading to dangerous side effects. For example:
- Blood thinners (like warfarin): Acetaminophen can increase the risk of bleeding.
- CNS depressants (like alcohol, opioids, sedatives): Increased risk of excessive sedation and respiratory depression.
- MAO inhibitors (used to treat depression): Potentially dangerous interactions with butalbital.
11. Effects on Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Fioricet is generally not recommended during pregnancy, especially because butalbital can cross the placenta and may cause neonatal withdrawal syndrome or developmental issues. It can also pass into breast milk and cause side effects in nursing infants.
12. Contraindications in Specific Medical Conditions
- People with certain health conditions, such as liver disease, kidney disease, respiratory conditions (like asthma or COPD), or porphyria, should not take Fioricet or should do so only under close medical supervision.
Summary of Main Concerns:
- Dependence and abuse potential (due to butalbital).
- Liver damage (due to acetaminophen).
- Impaired alertness and sedation (butalbital).
- Rebound headaches from overuse.
- Gastrointestinal issues (from caffeine).
- Respiratory depression (butalbital).
- Overdose risk from combined ingredients.
- Mental health effects (e.g., depression).
- Dangerous interactions with other medications.
Because of these concerns, Fioricet should be used cautiously, according to prescribed guidelines, and under close medical supervision to minimize risks.